
What is Hologram? | Ortmor Agency
If you are into Sci-Fi movies and books, then you must be familiar with the term ‘Hologram’. But if you are not sure about how it actually looks in real life then look no further than your pocket. There are holograms on your driver's license, credit card, and even on your ID cards. They are even present on some CDs, DVDs, and on pretty much everything that is sold under the label “official merchandise”. If that's not what you were expecting when searching for a hologram, then don’t be so disappointed. There’s more to Holograms than you expect.
For years, Hologram was a technology that only ruled Sci-Fi movies like Star Wars and Marvel movies. But thanks to advances in optical technology, there seem to be a few changes in that recently. Before we get into that, first let's just talk about what a hologram really is, its working, the history behind it and so much more.
If this looks like your cup of tea, then keep on reading…
What Really is a Hologram?
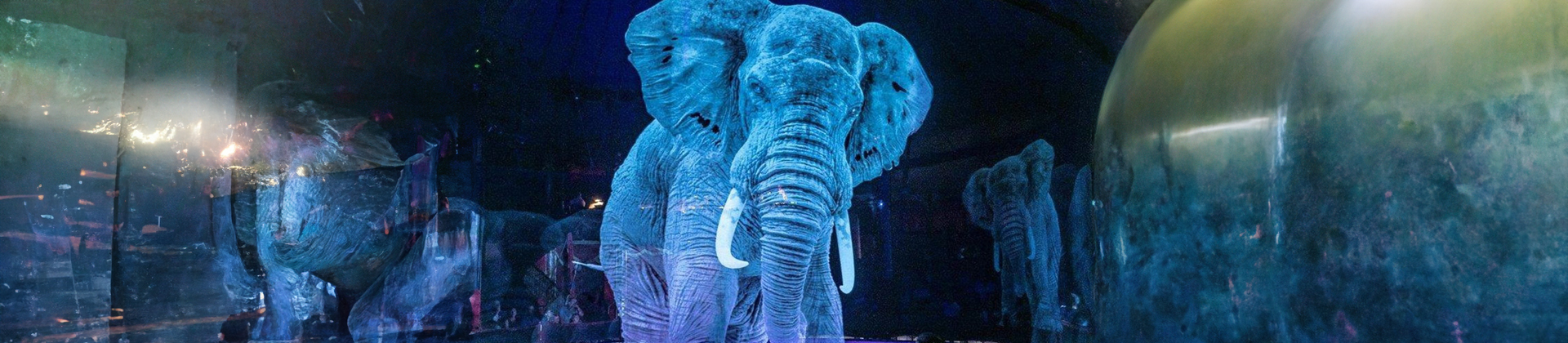

Holograms are virtual 3D images created using the interference of light beams that reflect real physical objects. What makes these holograms special from 3D projections is that they can be seen with the naked eye and they uniquely preserve the depth, parallax, and other properties of the original object. In simple terms, holograms are 3D images that are created when two light beams interfere and produce an image on a film or a surface. And the process of creating this photographic image of the object is called holography.
The Science Behind Hologram
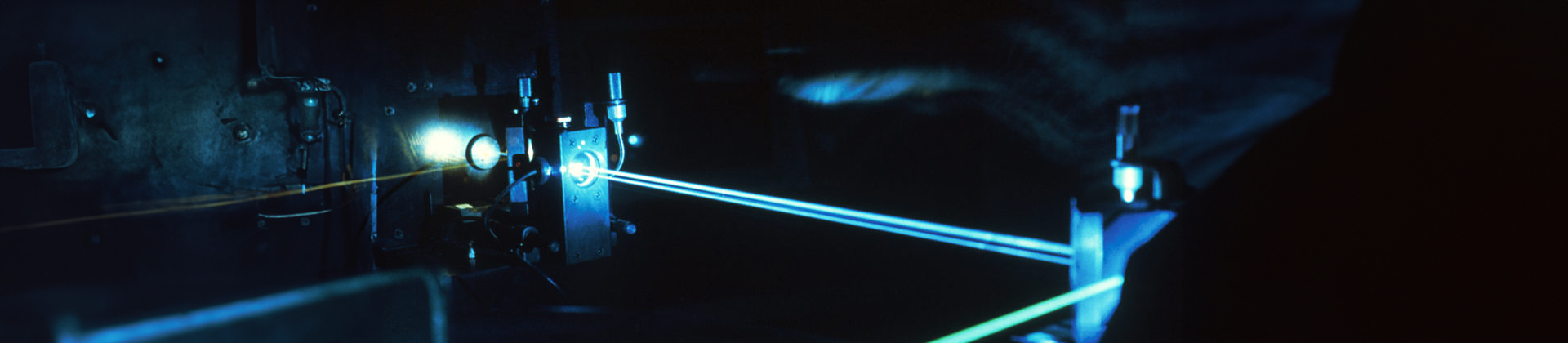
If you are interested in Hologram, then, of course, you must be interested in how a hologram works.
So to understand how does hologram works, first let's just look at how to create a hologram.
To create a hologram, firstly you need an object that needs to be recorded. Then a laser beam is shined upon the object and the recording medium. The recording medium has to be made with proper materials to get a clarified image. And lastly, you need an clear environment for the light beams to intersect. Then the laser beam is then split into two identical beams, the illumination beam, and the reference beam. Then the identical beam is redirected using mirrors and some of the light is reflected off the object onto the medium.
The reference beam is then directed to the recording medium so that it won't conflict with the imagery that comes from the illumination beam. Then the beams are coordinated with it to create a more precise image. The two beams interfere and intersect with each other. The interference pattern is what is displayed on the recorded medium, recreating the virtual image of the object.
One trick here is using photographic films with an extra amount of light-reactive grains as a recording medium as it will give a high resolution making the images look more realistic.
A Peek Into The History of Hologram
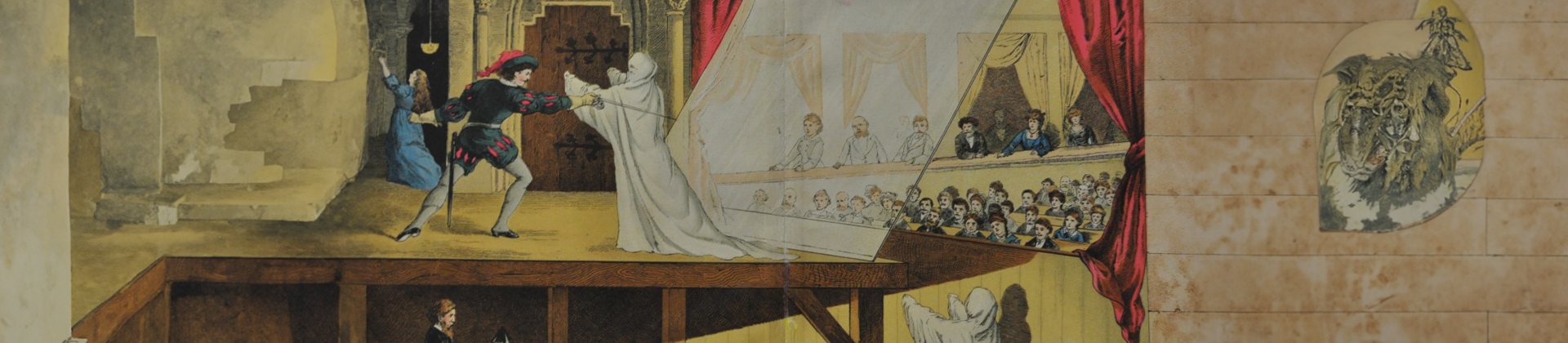

If you are a fan of star wars then you have probably seen princess Leia appearing as a floating image in the early episodes of Star Wars and Darth Vader speaking to his subordinates via a handheld holoprojector. And that right there is a Hologram. The history of the Hologram brings us straight to 1860 when the first holographic element was shown on a stage by the legendary John Henry Pepper.
So what is this pepper's ghost effect?
Pepper's ghost effect is an illusionary trick from the 19th century where the reflective properties of glass were used to create holographic displays.
In 1947, British scientist Dennis Gabor developed the theory of holography and the name holography was inspired by the Greek word 'holo' which means whole, and 'gramma' which means message. Later in 1962, Yuri Denisyuk in the soviet union and Emmet Leith and Juris Upatniek at the University of Michigan developed a white light reflection hologram that was viewable from an ordinary incandescent light bulb.
After Yuri Denisyuk there have been a few inventions, however, holograms never really developed to the point like how we see them in Sci-Fi Movies. Rather it became a technology that is only depicted in movies, games, and novels.
The Great Future Ahead
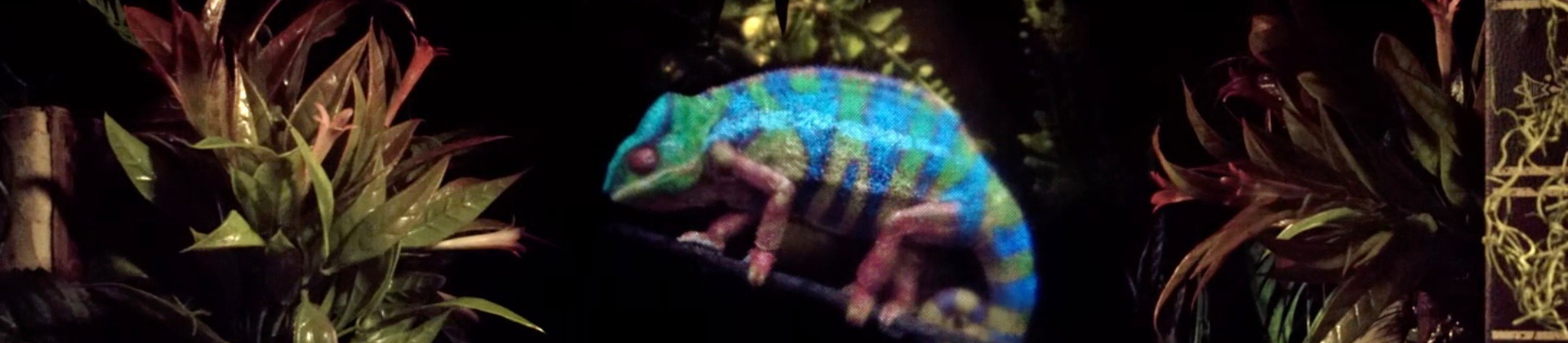

Times are changing and thanks to the advances in optical technology, 3D holograms have become a reality now. The San Jose Based Light Field Lab has created a hologram chameleon named Cammy and a wristwatch similar to a Rolex.
Now, they are on an expedition to make large-scale versions of holographic displays. And this innovation can change how we see the world. And they might even pop up in entertainment venues and theme parks where they'll create 3D images of dinosaurs, sharks, and dolphins to attract the audience.
Final Thoughts
Every day advancements in technology are changing the way we are living and how we see the world. With the advancement in optical technology, real-looking 3D holograms are finally here, to keep us wondering what is real and what is not. Who knows, they might even replace television to give an immersive experience in the future.

