
A Glimpse into the Past: The Intriguing History of Holograms
The world is absolutely fascinated with the Hologram technology. However, if you were to ask anyone about its origin, growth, and sudden popularity, they might not be well-informed. It's interesting to note that the Hologram was once one of the most beloved technologies of its time, about a quarter century ago.
Although it still has an impact today, it doesn't shine as brightly as it did in the late 90's. Not only has the public lost interest, but even scientists and engineers don't view it as a shining diamond anymore. So, what happened to Holograms? Can the evolving hologram technology bring back its lost glory? Let's take a journey through time and explore the fascinating world of holograms.
Hologram Throughout the years
Hologram has changed a lot throughout the years, Let's take a stroll through the fascinating evolution of holography year by year.
The Dawn of Holography: 1940s-1950s
Version 1: In the dimly lit laboratory of Dennis Gabor, a Hungarian-British physicist, a groundbreaking idea began to take shape. It was the late 1940s, and Gabor was contemplating the limitations of traditional photography. What if there was a method to not only capture the brightness of light but also its phase and amplitude? These thoughts eventually led to the creation of holography, a concept that would revolutionize our perception of reality.
Despite the challenges faced in practical applications in the years that followed, Gabor's theoretical work laid a strong foundation for future advancements. The lack of appropriate light sources and recording materials hindered progress, but his innovative vision inspired other scientists to explore new possibilities.
The Laser Revolution: 1960s
During the 1960s, holography entered a new era thanks to the invention of the laser. This breakthrough provided scientists with a powerful and consistent light source, which was crucial for creating high-quality holograms. Visionaries like Yuri Denisyuk in the Soviet Union and Emmett Leith and Juris Upatnieks in the United States were among the pioneers who recognized the immense potential of this discovery.

In research facilities across the globe, dedicated scientists worked tirelessly to refine holographic techniques. Although the initial holograms were rough and ethereal in appearance, they offered a tantalizing glimpse into the captivating world of imaging technology.
The Golden Age: 1970s-1980s
The 1970s witnessed a flurry of activity in the field of holography. Emmett Leith and Juris Upatnieks developed off-axis holography, a technique that greatly enhanced image quality and reduced unwanted artifacts. Meanwhile, holographic applications expanded beyond the confines of the laboratory.
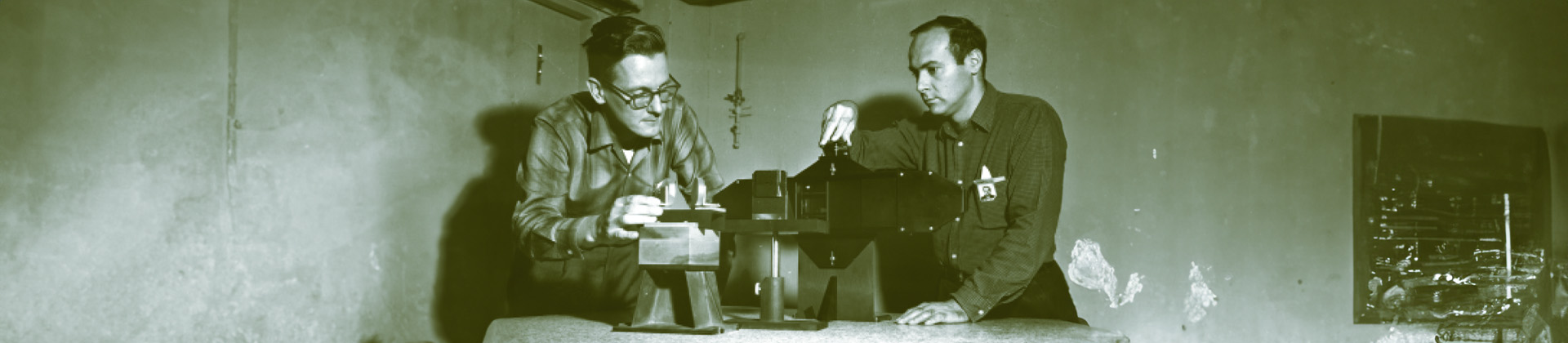

Artists embraced holography as a medium for creative expression, giving rise to a vibrant holographic art scene. Galleries and museums showcased dazzling holographic displays, captivating audiences with their otherworldly beauty.
The 1980s saw holography enter the mainstream consciousness. From advertising to entertainment, holographic images began to permeate popular culture. Concerts dazzled audiences with holographic special effects, while theme parks offered immersive holographic experiences.
Digital Horizons: 1990s

As the 1990s dawned, holography entered the digital age. Digital holography emerged, allowing for the creation of computer-generated holograms and the storage of holographic information in digital formats. This breakthrough opened up new frontiers in data storage, encryption, and medical imaging.
Meanwhile, research into holographic displays accelerated, fueled by the promise of more immersive visual experiences. Although practical challenges remained, the tantalizing prospect of three-dimensional holographic displays captured the imagination of scientists and engineers alike.
The Age of Accessibility: 2000s
By the turn of the millennium, holography had become more accessible than ever before. Advancements in laser technology and recording materials drove down costs, making holography feasible for a wider range of applications. From security to consumer electronics, holographic solutions found their way into everyday life.
The entertainment industry continued to push the boundaries of holographic technology, with spectacular displays captivating audiences around the globe. Yet, despite these advances, holographic displays remained somewhat niche, constrained by technical limitations and cost considerations.
Towards Tomorrow: 2010s and Beyond
The 2010s heralded a new chapter in the story of holography. As augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) gained traction, holographic displays emerged as a key enabler of immersive visual experiences. Companies like Magic Leap and Microsoft invested heavily in holographic technology, aiming to unlock its full potential.
2024: More Than Just a Science Fiction
In 2024, holographic technology has reached unprecedented levels of sophistication and integration into daily life. Holograms are no longer confined to science fiction; they're a ubiquitous part of our reality. From interactive holographic displays in public spaces to personalized holographic assistants in homes and offices, the applications are vast and varied. Teleconferencing feels more lifelike than ever, with participants appearing as fully rendered holograms, fostering genuine connections across distances.
Medical professionals utilize holographic imaging for precise diagnostics and surgical planning, revolutionizing healthcare. Entertainment experiences are immersive and dynamic, with holographic concerts, theater productions, and gaming environments captivating audiences worldwide. As holographic technology continues to evolve, its potential seems limitless, offering new possibilities for communication, creativity, and exploration in the digital age.
Final Thoughts
The evolution of holograms throughout history has been truly remarkable, transitioning from a mere concept to a tangible reality. From the groundbreaking work of physicists like Dennis Gabor to the widespread use of holographic technology in everyday life in 2024, each year has brought significant progress and innovation. What was once limited to scientific labs has now become an essential part of various industries, including entertainment, communication, healthcare, and security.
As we strive to advance holographic technology further, the future holds endless possibilities for more immersive and impactful experiences. Whether it's connecting people across distances, revolutionizing medical practices, or enhancing entertainment, holograms are set to shape our world in profound and exciting ways. As we step into the holographic future, one thing is clear: we are just scratching the surface of what holograms can achieve.

