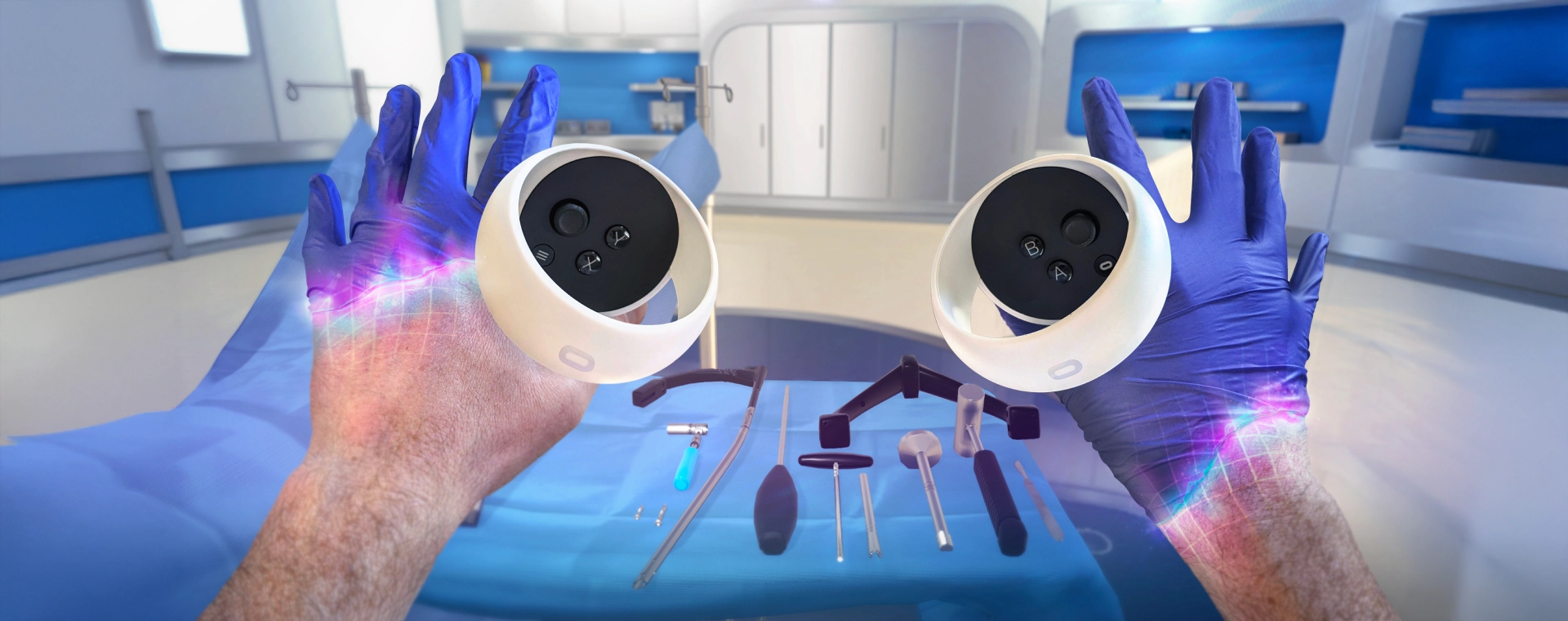

A New Era of Learning: Virtual Reality in Medical and Healthcare Training
Virtual Reality (VR) has transcended its futuristic origins to become a groundbreaking force in various industries. Among the sectors witnessing profound transformation through VR technology, the field of medical and healthcare training stands out as a prime example.
The integration of VR into medical and healthcare training programs has revolutionized the way aspiring medical professionals and healthcare workers prepare for their roles, offering an immersive, highly effective, and safe learning environment.
Enhanced Immersion in Medical Training with Virtual Reality
Medical education are often historically focused on textbooks, lectures, and a limited number of practical experiences. While these methods are valuable, they cannot replicate the immersive and interactive nature of VR. Medical training with virtual reality introduces students to lifelike scenarios where they can practice skills and make decisions in a controlled yet realistic environment.
Surgical Training: VR simulations have become a game-changer in surgical training. Surgeons can now practice complex procedures without the need for cadavers or live patients. They can hone their skills, develop muscle memory, and gain confidence through realistic simulations. The haptic feedback in VR adds to the sense of touch, allowing surgeons to feel tissue resistance, and enhancing their training experience.
Anatomy Education: Learning human anatomy is a fundamental aspect of medical training. VR allows students to explore 3D models of the human body, dissect virtual cadavers, and visualize complex anatomical structures from different angles. This immersive approach improves retention and understanding.
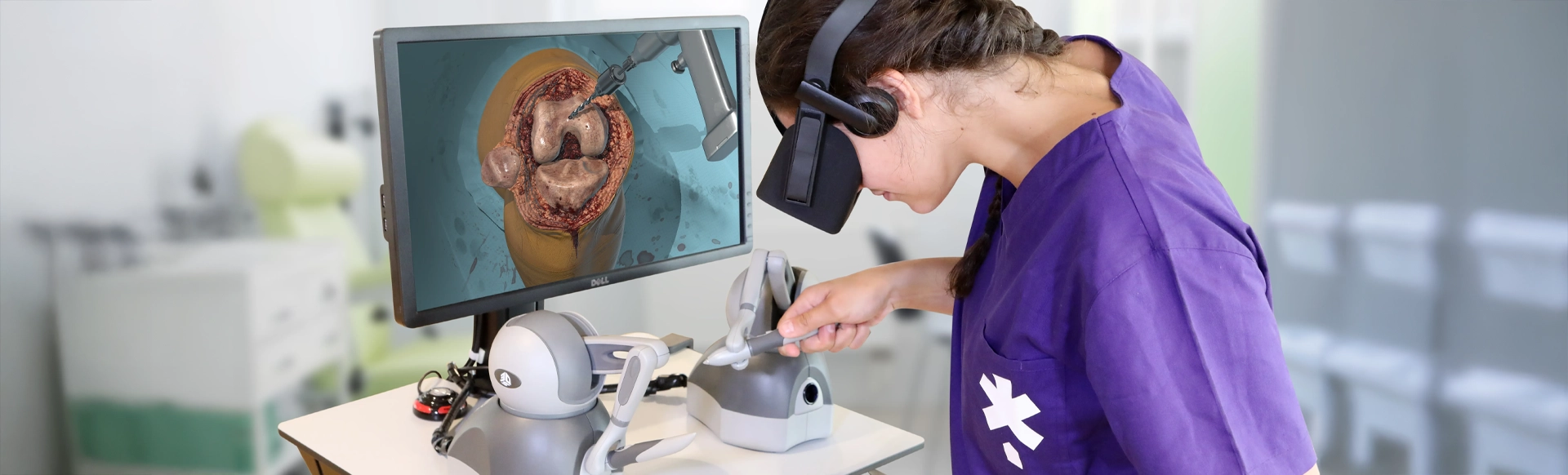
Patient Interaction: VR enables medical students to interact with virtual patients, practicing communication skills, bedside manner, and empathetic patient care. These scenarios can range from routine check-ups to dealing with emotionally charged situations, helping students build confidence and empathy.
Healthcare Training with Virtual Reality
In addition to medical professionals, VR is making a significant impact on the training of various healthcare workers, including nurses, paramedics, and therapists.
Nursing Education: VR simulations offer nursing students the opportunity to practice essential skills such as patient assessment, medication administration, and wound care. They can encounter diverse patient scenarios, from routine care to critical emergencies, improving their clinical judgment and decision-making skills.
Paramedic Training: Paramedics often face high-stress situations in their line of duty. VR allows them to train for emergencies like cardiac arrests, traumatic injuries, and mass casualty incidents in a safe and controlled environment. Realistic simulations help paramedics react more effectively and efficiently during real-life emergencies.
Therapy and Rehabilitation: VR has also found its way into physical and occupational therapy training. Therapists can create customized VR exercises to aid patients in their recovery processes. Patients can immerse themselves in therapeutic environments that make rehabilitation more engaging and enjoyable.
Safe and Risk-Free Learning
One of the most significant advantages of medical training with virtual reality is the risk-free learning environment it offers. In traditional training, mistakes during surgeries or patient care can have serious consequences. VR eliminates these risks, allowing students to learn from their errors without harming real patients.
Error Management: Students can deliberately make mistakes in VR simulations and learn from them. This iterative process helps them develop problem-solving skills and critical thinking, which are crucial in healthcare settings.
Stress Management: High-stress scenarios can be recreated in VR to prepare healthcare professionals for real-life situations. This exposure helps reduce anxiety and improves performance during stressful events.
Accessibility and Cost-Efficiency
Medical and healthcare training programs often face challenges related to access to resources and cost. VR technology can bridge these gaps by making training more accessible and cost-effective.
Remote Learning: VR allows students to access training modules from anywhere, reducing the need for physical classrooms and costly travel. This is especially beneficial for rural or remote areas with limited access to healthcare education.
Reduced Equipment Costs: While the initial investment in VR equipment can be significant, it can lead to substantial cost savings in the long run. Simulations replace the need for expensive medical equipment, cadavers, and consumables.
Personalized Learning
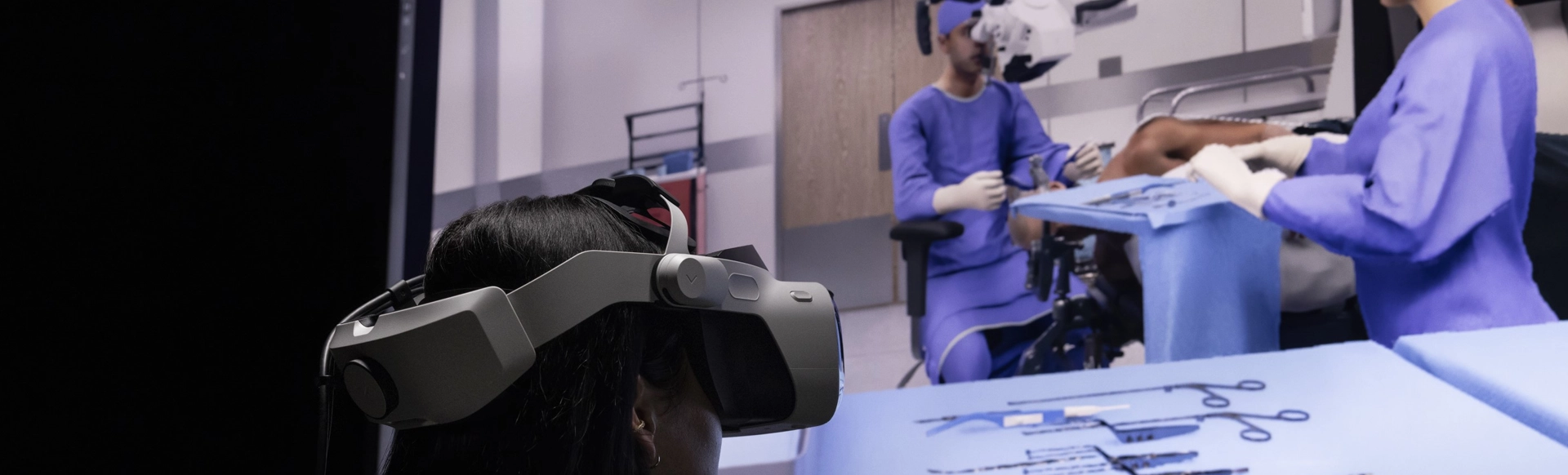

VR in medical and healthcare training can be tailored to individual learning needs. This personalized approach ensures that students receive the education and practice they require, helping them progress at their own pace. Here is an example;
Skill Progression: VR platforms can track students' performance and provide feedback on areas that need improvement. This data-driven approach allows instructors to design targeted interventions to enhance students' skills.
Customized Scenarios: Instructors can create customized VR scenarios to meet specific training objectives. Whether it's practicing a rare surgical procedure or refining clinical assessment skills, VR can accommodate diverse learning goals.
Ending Line
The integration of virtual reality into medical and healthcare training has opened up new frontiers in education. It provides a safe, immersive, and cost-effective way for aspiring medical professionals and healthcare workers to develop their skills and knowledge. From surgical simulations to patient interactions and beyond, VR has the potential to transform the healthcare industry by producing better-trained professionals who are better equipped to handle the challenges of their roles. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative applications of VR in the field of medical and healthcare training, further improving the quality of care provided to patients worldwide.